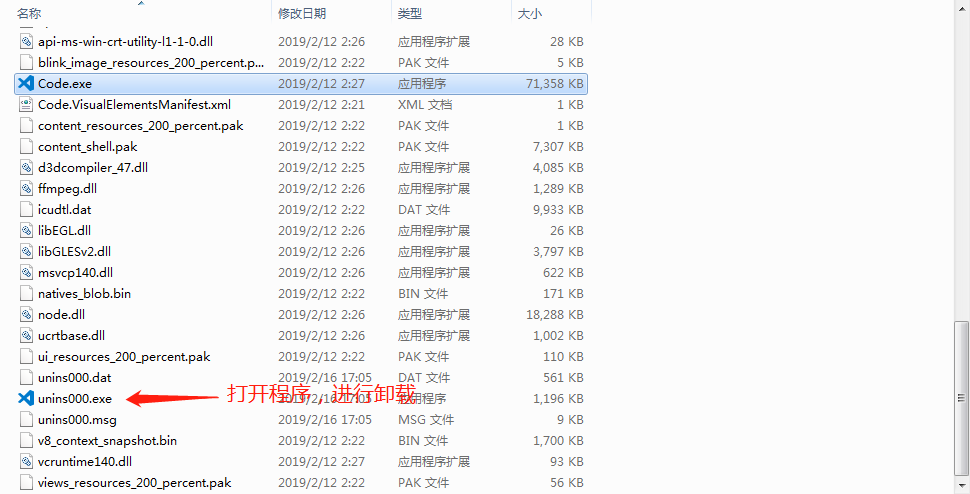
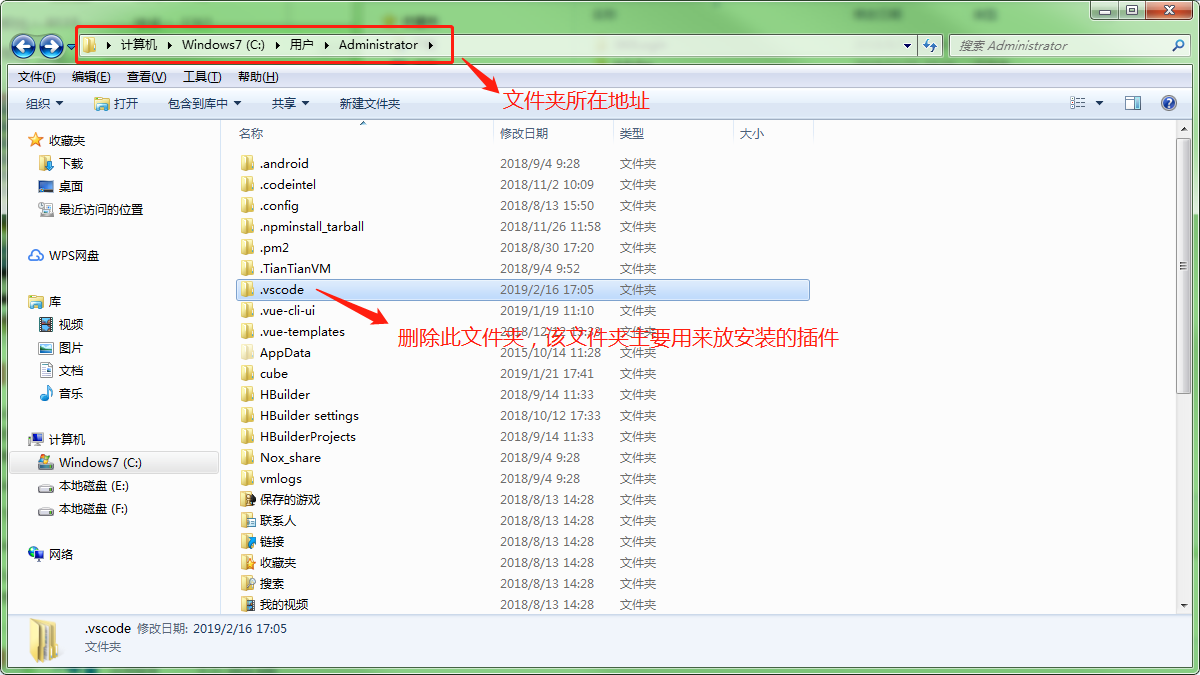
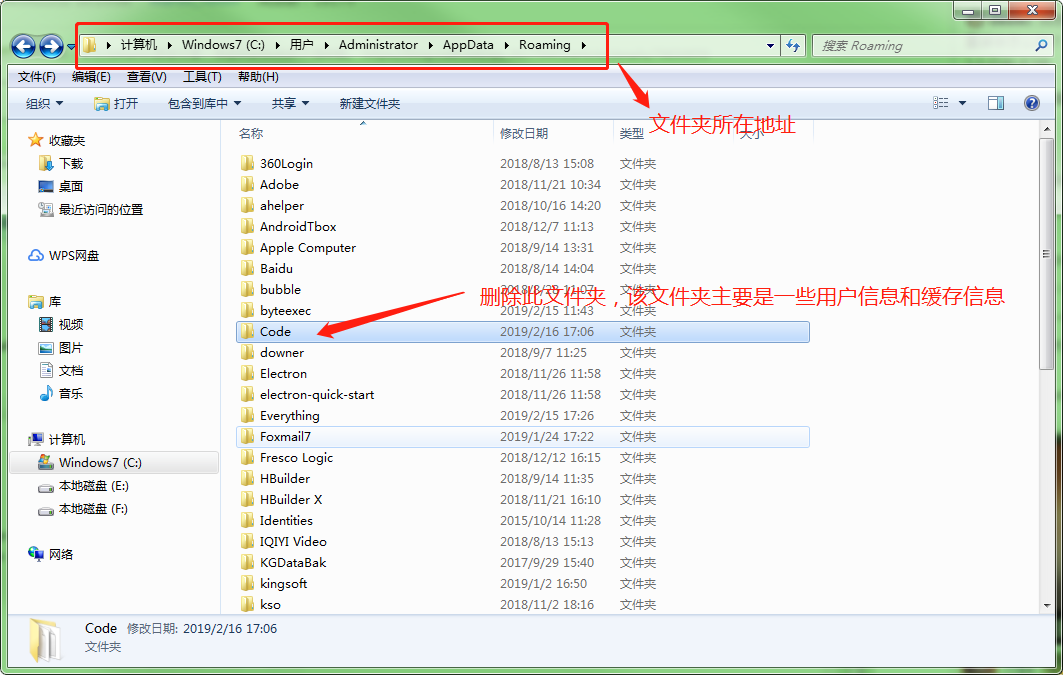
| 10.1% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Win10 |
| 8.7% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Win10 |
| 6.0% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
Win10 |
| 4.8% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Win10 |
| 4.7% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.164 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Win10 |
| 3.8% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
macOS |
| 2.9% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
macOS |
| 2.6% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/14.1.1 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari Generic
macOS |
| 2.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.114 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
macOS |
| 2.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/14.1.2 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari Generic
macOS |
| 2.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
Linux |
| 2.0% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.164 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
macOS |
| 2.0% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
macOS |
| 1.9% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; rv:78.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/78.0 |
Firefox 78.0
Win10 |
| 1.7% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
Linux |
| 1.5% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:89.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/89.0 |
Firefox 89.0
Win10 |
| 1.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 Edg/92.0.902.55 |
Edge 92.0
Win10 |
| 1.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0 |
Firefox 91.0
Win10 |
| 1.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 Edg/92.0.902.67 |
Edge 92.0
Win10 |
| 1.1% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 Edg/92.0.902.62 |
Edge 92.0
Win10 |
| 1.0% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Linux |
| 0.9% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:78.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/78.0 |
Firefox 78.0
Linux |
| 0.7% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Linux |
| 0.7% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.114 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Linux |
| 0.6% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 Edg/91.0.864.70 |
Edge 91.0
Win10 |
| 0.6% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.164 Safari/537.36 OPR/77.0.4054.277 |
Opera Generic
Win10 |
| 0.6% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.164 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Linux |
| 0.6% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Win7 |
| 0.5% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:89.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/89.0 |
Firefox 89.0
macOS |
| 0.5% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.164 Safari/537.36 Edg/91.0.864.71 |
Edge 91.0
Win10 |
| 0.5% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.115 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Win10 |
| 0.5% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_6) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/14.1.1 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari Generic
macOS |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0 |
Firefox 91.0
macOS |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_6) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/14.0.3 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari 14.0
macOS |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Win7 |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:78.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/78.0 |
Firefox 78.0
Win10 |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
Win7 |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0 |
Firefox 91.0
Win10 |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/14.1 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari Generic
macOS |
| 0.4% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0 |
Firefox 91.0
Linux |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Fedora; Linux x86_64; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
Linux |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:89.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/89.0 |
Firefox 89.0
Linux |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 Edg/91.0.864.67 |
Edge 91.0
Win10 |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/76.0.3809.100 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 76.0
Win10 |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.114 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Win10 |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0 |
Firefox 91.0
Linux |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/15.0 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari Generic
macOS |
| 0.3% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.77 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Win10 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 OPR/77.0.4054.203 |
Opera Generic
Win10 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Win8.1 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_13_6) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/13.1.2 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari 13.1
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.114 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Win7 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:89.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/89.0 |
Firefox 89.0
Linux |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.164 Safari/537.36 OPR/77.0.4054.275 |
Opera Generic
Win10 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.14; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
Win8.1 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 Edg/92.0.902.73 |
Edge 92.0
Win10 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 OPR/78.0.4093.147 |
Opera Generic
Win10 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/13.1.3 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari 13.1
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.93 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 90.0
Win10 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.13; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_6) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/14.1.2 Safari/605.1.15 |
Safari Generic
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; Win64; x64; rv:90.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/90.0 |
Firefox 90.0
Win8.1 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.15; rv:78.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/78.0 |
Firefox 78.0
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_6) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.164 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 91.0
macOS |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0 |
Firefox 91.0
Win7 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.131 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 92.0
Win8.1 |
| 0.2% |
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36 |
Chrome 90.0
Linux |